

Next: Example Applications
Up: Algorithm
Previous: New Mutation Operator: Parabolic
We use a canonical EA, as shown in figure 3. Each of the modules is self-contained and is explained below.
- Initialization
Each gene in each chromosome is randomly initialized within its domain constraints.
- Evaluation
Each chromosome is evaluated with a specified fitness function.
- New Population Generation
The new population is formed in four steps:
- Elitist. This is a common method of ensuring that the best chromosome from the last population is preserved
intact. It is simply copied as the first member of the new population.
- Crossover. We use tournament selection to produce the next tranche of population.
- Mutation. We switch between parabolic search mutation and random mutation every iteration.
- Re-initialization. Some of the new population is entirely re-randomized each iteration. This is normally a very
low percentage of the chromosomes in the population.
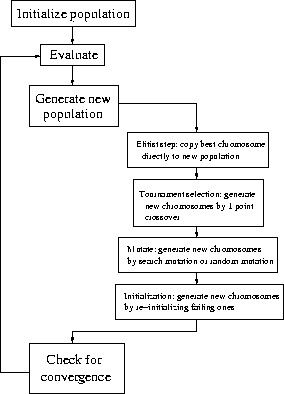
Figure 3: Algorithm Context
Craig Robertson
Tue Sep 10 11:25:09 BST 2002
