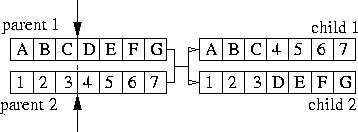
Figure 1: Canonical 1-point EA Crossover
The main operator of EAs is the crossover, which carries useful information forwards through population generations. There are many probabilistic ways of selecting chromosomes to crossover. Most are based on some ranking of chromosomes by their fitness value. One example of this is to generate a probability of selection by cumulative summing of the ascending sorted normalised fitness values and using the values as a probability of selection.
Another method is to pick two sets of two chromosomes from the population at random and choose the best of each pair, known as tournament selection.
Crossover itself is generally a matter of overwriting two chromosomes (parents) with the two others (offspring). The offspring are formed by overwriting a random number genes from one parent onto the chromosome of the other. This is done symmetrically to form the two offspring, as shown in figure 1.

Figure 1: Canonical 1-point EA Crossover